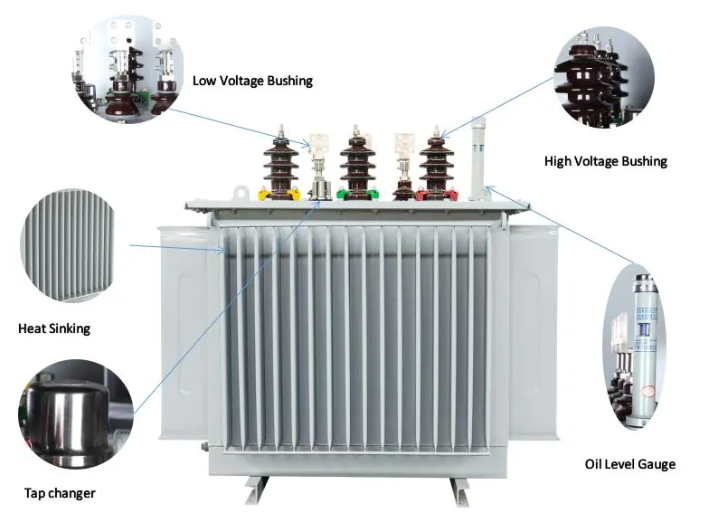
Basic Structure of oil-immersed transformer:
The oil-immersed transformer mainly consists of core, windings, oil tank, insulation bushings, radiators and other components. The core is usually made of laminated silicon steel sheets to reduce eddy current losses. The windings are wound with copper or aluminum wires and achieve voltage transformation through the principle of electromagnetic induction. The oil tank is used to hold the transformer oil, which plays the roles of insulation, cooling and heat dissipation.
Working Principle:
It is based on the law of electromagnetic induction, and changes the magnitude of AC voltage through the turns ratio of the primary winding and the secondary winding. When the primary winding is connected to an AC power source, an alternating magnetic flux is generated in the core, thereby inducing a corresponding voltage in the secondary winding.
Features:
- Good insulation performance: Transformer oil has good insulation performance, which can effectively prevent short circuits between windings and between windings and the core.
- Efficient heat dissipation: The good fluidity of oil can quickly take away the heat generated during the operation of the transformer to ensure that the transformer works within the normal temperature range.
- Strong overload capacity: It can withstand a certain degree of overload for a short time to adapt to unexpected situations in the power system.
Application Fields:
Oil-immersed transformers are often used in power plants, substations, industrial and mining enterprises and other places to provide appropriate voltage levels for power transmission, distribution and use.
If you want to know more information,welcome to contact us !