ការជ្រើសរើសត្រង់ស្វូម៉ែតអគ្គិសនីដែលសមស្របសម្រាប់កម្មវិធីឧស្សាហកម្ម ទាមទារការពិចារណាយ៉ាងប្រុងប្រយ័ត្នលើកត្តាបច្ចេកទេស និងប្រតិបត្តិការជាច្រើន។ ប្រព័ន្ធចែកចាយថាមពលពឹងផ្អែកយ៉ាងខ្លាំងលើគ្រឿងបញ្ចូលសំខាន់ៗទាំងនេះ ដើម្បីធានាការគ្រប់គ្រងវ៉ុលប្រកបដោយប្រសិទ្ធភាព និងសុវត្ថិភាពអគ្គិសនីនៅទូទាំងសហគ្រាសពាណិជ្ជកម្ម និងឧស្សាហកម្ម។ ការយល់ដឹងពីតម្រូវការជាក់លាក់នៃហេដ្ឋារចនាសម្ព័ន្ធអគ្គិសនីរបស់អ្នក នឹងជួយអ្នកធ្វើការសម្រេចចិត្តដោយមានចំណេះដឹង នៅពេលវិនិយោគលើបច្ចេកវិទ្យាត្រង់ស្វូម៉ែត។

សហគ្រាសឧស្សាហកម្មពឹងផ្អែកលើសម្ភារៈចែកចាយថាមពលដែលអាចទុកចិត្តបាន ដើម្បីរក្សាប្រតិបត្តិការបន្ត និងការពារសម្ភារៈអេឡិចត្រូនិចដែលប្រើប្រាស់ដោយប្រុងប្រយ័ត្នពីការរំញ័រវ៉ុល។ ដំណើរការជ្រើសរើសពាក់ព័ន្ធនឹងការវាយតម្លៃតម្រូវការថាមពល លក្ខខណ្ឌបរិស្ថាន ស្តង់ដារសុវត្ថិភាព និងការពិចារណាអំពីការថែទាំរយៈពេលវែង។ ដំណើរការផលិតទំនើបទាមទារការគ្រប់គ្រងវ៉ុលដោយជាក់លាក់ និងការផ្តល់ថាមពលដែលមានស្ថេរភាព ដើម្បីធានាគុណភាពផលិតផល និងប្រសិទ្ធភាពប្រតិបត្តិការ។
វិស្វករអគ្គិសនី និងអ្នកគ្រប់គ្រងសំណាញ់ភ្លើងត្រូវតែធ្វើតុល្យភាពរវាងការវិនិយោគដើមទុន និងថ្លៃដើមប្រតិបត្តិការ តម្រូវការភាពជឿជាក់ និងតម្រូវការពង្រីកនាពេលអនាគត។ ផ្សារទ្រង់ទ្រាយម៉ាស៊ីនបំលែងភ្លើងផ្តល់ជូននូវបច្ចេកវិទ្យា និងរចនាសម្ព័ន្ធផ្សេងៗគ្នា ដែលត្រូវបានរចនាឡើងដើម្បីឆ្លើយតបតាមតម្រូវការឧស្សាហកម្ម និងស្តង់ដារគ្រប់គ្រងជាក់លាក់។ ការយល់ដឹងអំពីជម្រើសទាំងនេះនឹងអនុញ្ញាតឱ្យធ្វើការសម្រេចចិត្តទិញដោយដឹងខ្លួន ដែលគាំទ្រគោលដៅអាជីវកម្ម និងតម្រូវការសុវត្ថិភាពអគ្គិសនី។
ការយល់ដឹងអំពីបច្ចេកវិទ្យា និងកម្មវិធីម៉ាស៊ីនបំលែងភ្លើង
គោលការណ៍រចនាចម្បង និងមេកានិចប្រតិបត្តិការ
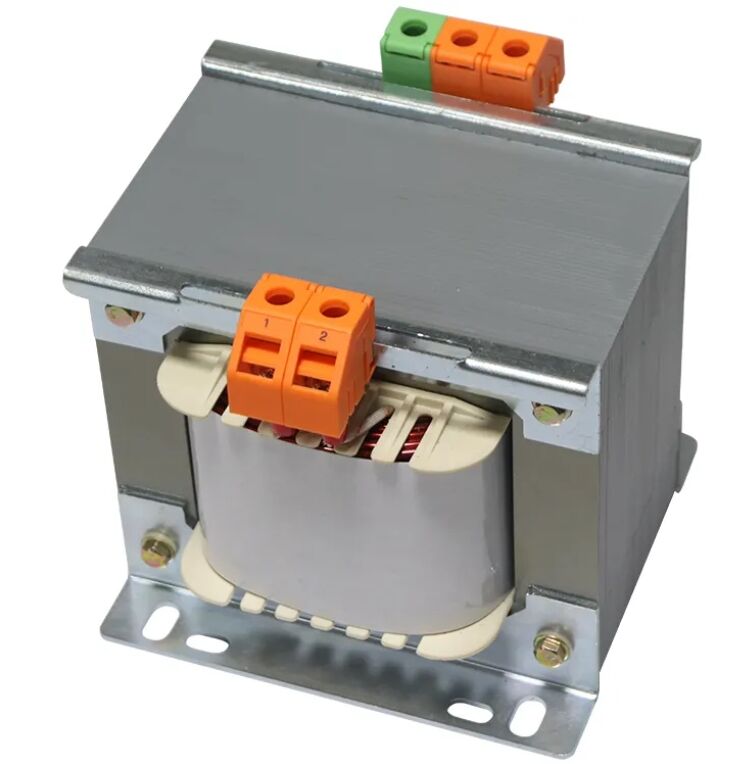
ត្រង់ស្វូរម៉ែតក្នុងវិស័យអគ្គិសនីដំណើរការដោយផ្អែកលើគោលការណ៍ជាមូលដ្ឋាននៃអ៊ីនឌុចស្យូនអេឡិចត្រូម៉ាញ៉េទិច ដោយប្រើខ្សែពួរបឋម និងទុតិយភូមិដែលពួរជុំវិញចិញ្ចៀនប៉ោងម៉ាញ៉េទិច ដើម្បីផ្ទេរថាមពលអគ្គិសនីរវាងកម្រិតវ៉ុលផ្សេងៗគ្នា។ ចិញ្ចៀនប៉ោងម៉ាញ៉េទិច ដែលជាធម្មតាត្រូវបានសាងសង់ពីសន្លឹកដែកស៊ីលីកុន ផ្តល់ផ្លូវប្រសើរសម្រាប់ចរន្តមហាឡិចត្រូម៉ាញ៉េទិច ខណៈពេលដែលកាត់បន្ថយការបាត់បង់ថាមពលតាមរយៈប្រាក់ដែកអ៊ីដី និងផលប៉ះពាល់ហ៊ីសធើរេសិស។ ការរចនានេះអនុញ្ញាតឱ្យមានការប្តូរវ៉ុលដោយគ្មានកំហុស ខណៈពេលដែលរក្សាការបំបែកអគ្គិសនីរវាងសៀគ្គ្រឹះបញ្ចូល និងបញ្ចេញ។
ការរៀបចំខ្សែវេនរ៉ាប់កំណត់អត្រាការប្តូរវ៉ុល ដោយត្រង់ស្វូម៉ែរបំប្លែងឡើងវិញនូវកំរិតវ៉ុលសម្រាប់ការប្រើប្រាស់ក្នុងការផ្ញើរ ហើយត្រង់ស្វូម៉ែរបំប្លែងចុះវិញនូវវ៉ុលសម្រាប់ការចែកចាយ និងការប្រើប្រាស់។ ប្រព័ន្ធបន្ស៊ីមានតួនាទីសំខាន់ក្នុងការរក្សាសីតុណ្ហភាពប្រតិបត្តិការឱ្យបានល្អប្រសើរ និងការពារការបំផ្លាញខ្សែច្រវាក់ដោយកំដៅ។ ការរាយប៉ាយកំដៅបានត្រឹមត្រូវធានានូវភាពអាចទុកចិត្តបានក្នុងរយៈពេលវែង និងពន្យារអាយុកាលប្រើប្រាស់របស់ត្រង់ស្វូម៉ែរក្រោមស្ថានភាពផ្ទុកដែលប្រែប្រួល។
ការរចនាត្រង់ស្វូម៉ែរទំនើបបានបញ្ចូលលក្ខណៈការពារដូចជាវ៉ែលបំបែកសម្ពាធខ្ពស់ ប្រព័ន្ធតាមដានសីតុណ្ហភាព និងសៀនស៊ើមានសមត្ថភាពរកឃើញការបំផ្លាញខ្សែច្រវាក់ ដើម្បីបង្កើនសុវត្ថិភាព និងភាពអាចទុកចិត្តបានក្នុងការប្រើប្រាស់។ សមត្ថភាពតាមដានទាំងនេះអនុញ្ញាតឱ្យអនុវត្តយុទ្ធសាស្ត្រថែទាំបែបប្រព្រឹត្ត ដែលជួយកាត់បន្ថយការបែកខ្ទេចខ្ទីដោយគ្មានការព្រមាន និងពន្យារអាយុកាលប្រើប្រាស់របស់បរិក្ខារ។ ការយល់ដឹងអំពីផ្នែកបច្ចេកទេសទាំងនេះជួយដល់អ្នកគ្រប់គ្រងសំណាក់ក្នុងការជ្រើសរើសសេចក្តីបញ្ជាក់បច្ចេកទេសត្រង់ស្វូម៉ែរដែលសមស្របសម្រាប់ការប្រើប្រាស់ជាក់លាក់របស់ពួកគេ។
កម្មវិធីឧស្សាហកម្ម និងតម្រូវការបន្ទុក
សំណាក់ផលិតកម្ម ត្រូវការម៉ាស៊ីនបំលែងដែលអាចទប់ទល់នឹងគ្រប់ប្រភេទបន្ទុក រួមទាំងចរន្តចាប់ផ្តើមរបស់ម៉ូទ័រ សម្ភារៈកែតម្រឹមសមាមាត្រថាមពល និងបន្ទុកអេឡិចត្រូនិចដែលប្រើថាមពលថេរដែលត្រូវការការគ្រប់គ្រងវ៉ុល្សថេរ។ ដំណើរការឧស្សាហកម្មធ្ងន់ដូចជាការផលិតថែប ការដំណើរការគីមី និងសកម្មភាពរ៉ែ បង្កើតតម្រូវការអគ្គិសនីធ្ងន់ធ្ងរ ដែលតម្រូវឱ្យមានការរចនាម៉ាស៊ីនបំលែងរឹងមាំ ដែលមានសមត្ថភាពទប់ទល់នឹងការកំហុសខ្លីបានល្អប្រសើរ។ កម្មវិធីទាំងនេះភាគច្រើនពាក់ព័ន្ធនឹងលក្ខខណ្ឌបរិស្ថានធ្ងន់ធ្ងរ ដែលតម្រូវឱ្យមានប្រអប់ការពារពិសេស និងប្រព័ន្ធฉន្ទះការពារបន្ថែម។
អាគារពាណិជ្ជកម្ម និងមជ្ឈមណ្ឌលទិន្នន័យផ្តោតលើប្រសិទ្ធភាពថាមពល និងគុណភាពថាមពល ដែលត្រូវការត្រង់ស្វូរម៉ាស៊ីនដែលមានការខាតបង់ថាមពលទាប និងលក្ខណៈប្រែប្រួលវ៉ុលបានល្អ។ មន្ទីរពេទ្យទាមទារភាពអាចទុកចិត្តបានខ្ពស់ និងសមត្ថភាពថាមពលបម្រុងដើម្បីគាំទ្រសម្ភារៈសំខាន់ៗសម្រាប់ជីវិត និងរក្សាការប្រតិបត្តិការបន្តក្នុងអំឡុងពេលខ្វះថាមពល។ ស្ថាប័នអប់រំ និងអាគារការិយាល័យទទួលបានអត្ថប្រយោជន៍ពីត្រង់ស្វូរម៉ាស៊ីនដែលត្រូវបានរចនាសម្រាប់គំរូផ្ទុកប្រែប្រួល និងការអនុវត្តការសន្សំថាមពល។
សំណង់ផលិតថាមពលប្រើប្រាស់ត្រង់ស្វូរម៉ាស៊ីនសម្រាប់ការសម្របសម្រួលកម្រិតវ៉ុលរវាងម៉ាស៊ីនកំដៅ ប្រព័ន្ធផ្ទេរ និងការផ្គត់ផ្គង់ថាមពលបន្ថែម។ ការដំឡើងថាមពលដែលអាចផ្តល់ឡើងវិញបានទាមទារការរចនាត្រង់ស្វូរម៉ាស៊ីនពិសេស ដែលឆបគ្នានឹងគំរូការផលិតប្រែប្រួល និងតម្រូវការធ្វើឱ្យស៊ើបស៊ីនជាមួយបណ្តាញ។ ការយល់ដឹងអំពីតម្រូវការកម្មវិធីផ្សេងៗទាំងនេះ ធ្វើឱ្យអាចជ្រើសរើស និងអភិវឌ្ឍការបញ្ជាក់ត្រង់ស្វូរម៉ាស៊ីនបានត្រឹមត្រូវ។
សេចក្តីបញ្ជាក់បច្ចេកទេស និងលក្ខខណ្ឌប្រតិបត្តិការ
ការពិចារណាលើថាមពល និងថ្នាក់វ៉ុល
ថាមពលរបស់ម៉ាស៊ីនបំលែងត្រូវតែអាចទ្រទ្រង់ទាំងការប្រើប្រាស់ធម្មតា និងតម្រូវការកំពូលដែលបានរំពឹងទុក ព្រមទាំងផ្តល់សមត្ថភាពគ្រប់គ្រាន់សម្រាប់ការពង្រីកនាពេលអនាគត។ ការកំណត់ទំហំឱ្យបានត្រឹមត្រូវ ទាមទារឱ្យគណនាទំហំបន្ទុកដែលបានភ្ជាប់ កត្តាប្រើប្រាស់ និងកត្តាភាពខុសប្លែក ដើម្បីកំណត់ថាមពល kVA ដែលល្អបំផុត ដែលធានាតម្លៃដំបូងនិងភាពអាចបត់បែនបានក្នុងការប្រើប្រាស់។ ម៉ាស៊ីនបំលែងដែលធំពេក អាចដំណើរការមិនមានប្រសិទ្ធភាពនៅពេលបន្ទុកស្រាល ខណៈដែលម៉ាស៊ីនតូចពេក អាចប្រឈមនឹងការក្តៅហួស និងការខូចមុនពេលកំណត់នៅពេលបន្ទុកកំពូល។
ការជ្រើសរើសថ្នាក់វ៉ុលអាស្រ័យលើលក្ខណៈសម្បត្តិនៃការផ្គត់ផ្គង់ថាមពល ការរចនាប្រព័ន្ធចែកចាយ និងតម្រូវការបន្ទុកនៅទូទាំងសំណាក់។ ថ្នាក់វ៉ុលស្តង់ដារ រួមមានប្រព័ន្ធវ៉ុលទាបដែលមានវ៉ុលរហូតដល់ 1000V ប្រព័ន្ធវ៉ុលមធ្យមពី 1kV ដល់ 35kV និងប្រព័ន្ធវ៉ុលខ្ពស់លើសពី 35kV។ ថ្នាក់វ៉ុលនីមួយៗទាមទារឱ្យមានការដាក់អ៊ីសូឡង់ជាក់លាក់ ចន្លោះសុវត្ថិភាព និងសេចក្តីកំណត់សម្រាប់សម្ភារៈការពារ ដែលប៉ះពាល់ដល់ការរចនា និងថ្លៃដើមដំឡើងត្រង់ស្វូរ។
ការពិចារណាលើគុណភាពថាមពល រួមមានការគ្រប់គ្រងវ៉ុល ការខូចទ្រង់ទ្រាយអារម៉ូនិក និងលក្ខណៈប្រតិកម្មបណ្តោះអាសន្ន ដែលប៉ះពាល់ដល់សមត្ថភាពប្រើប្រាស់របស់សម្ភារៈដែលមានភាពប្រុងប្រយ័ត្ន។ ការ ម៉ាស៊ីនប្តូរអ៊ីល ផ្តល់នូវការគ្រប់គ្រងវ៉ុល និងសមត្ថភាពអារម៉ូនិកល្អប្រសើរសម្រាប់កម្មវិធីឧស្សាហកម្មដែលត្រូវការការផ្គត់ផ្គង់ថាមពលដ៏មានស្ថេរភាព។ លក្ខណៈរបស់ភាពត្រឹមត្រូវកំណត់កម្រិតចរន្តខ្លី និងការសម្របសម្រួលជាមួយសម្ភារៈការពារនៅទូទាំងប្រព័ន្ធចែកចាយអគ្គិសនី។
តម្រូវការបរិស្ថាន និងការដំឡើង
បរិស្ថានដែលដំឡើងមានឥទ្ធិពលយ៉ាងខ្លាំងទៅលើតម្រូវការរចនារបស់ត្រាស្វុីស្យូរ រួមទាំងការវាយតម្លៃសីតុណ្ហភាព ការពារសំណើម និងភាពធន់ទ្រាំនឹងការបំពុល។ ការដំឡើងខាងក្រៅត្រូវការប្រអប់ការពារពីអាកាសធាតុ ដែលមានការពារការរលួយកាន់តែប្រសើរ និងសម្ភារៈធន់នឹងកាំរស្មីយូវី ដើម្បីទប់ទល់នឹងការប៉ះពាល់រយៈពេលវែងទៅនឹងធាតុបរិស្ថាន។ ការដំឡើងខាងក្នុងអាចទទួលបានអត្ថប្រយោជន៍ពីតម្រូវការប្រអប់ថយចុះ ប៉ុន្តែត្រូវពិចារណាលើតម្រូវការខ្យល់ចេញចូល និងបទបញ្ញាត្តិសុវត្ថិភាពអគ្គិភ័យ។
ការពិចារណាលើសកលើការបើកបរមានសារៈសំខាន់នៅតាមតំបន់ដែលមានគ្រោះរញ្ជួយដី ដោយតម្រូវឱ្យមានប្រព័ន្ធដំឡើងពិសេស និងការពង្រឹងរចនាសម្ព័ន្ធ ដើម្បីការពារកុំឱ្យឧបករណ៍ខូចខាតក្នុងអំឡុងពេលមានហេតុការណ៍រញ្ជួយដី។ ផលប៉ះពាល់នៃកំពស់លើសមត្ថភាពฉន្ទះ និងប្រសិទ្ធភាពការបន្សិតត្រូវតែវាយតម្លៃសម្រាប់ការដំឡើងដែលកាន់តែខ្ពស់ជាងកំរិតកំពស់ស្តង់ដារ។ ការប្រែប្រួលសីតុណ្ហភាពបរិយាកាសប៉ះពាល់ដល់សមត្ថភាពផ្ទុករបស់ត្រាស្វុីស្យូរ ហើយអាចតម្រូវឱ្យមានការគណនាការថយចុះ ឬប្រព័ន្ធបន្សិតកាន់តែប្រសើរ។
កម្រិតសំឡេងរំខានក្នុងតំបន់អាគារស្នាក់នៅ ឬតំបន់ពាណិជ្ជកម្ម ប្រហែលត្រូវការការរចនាប្រឆាំងសំឡេង ឬបច្ចេកទេសដំឡើងពិសេស ដើម្បីបន្ថយការបញ្ចេញសំឡេង។ ការពិចារណាលើការរំខានដោយវិទ្យុសកម្មក៏កាន់តែសំខាន់នៅកន្លែងដែលមានឧបករណ៍អេឡិចត្រូនិច ឬប្រព័ន្ធទំនាក់ទំនងប្រើប្រាស់។ តម្រូវការគោរពតាមបទបញ្ញត្តិបរិស្ថាន រួមមានការដោះស្រាយអ៊ុល និងការគោរពតាមបទបញ្ញត្តិក្នុងស្រុក ដែលទាក់ទងនឹងការដំឡើង និងប្រតិបត្តិការត្រង់ស្វូម៉ែត។
ការថែទាំ និងការវិភាគថ្លៃដើមអាយុកាល
យុទ្ធសាស្ត្រថែរក្សាមុនបាន
កម្មវិធីថែទាំដែលមានប្រសិទ្ធភាពសម្រាប់ត្រង់ស្វើម ដែលបំពេញដោយប្រេង រួមមានការធ្វើតេស្តប្រេងអន្តរកម្មជាទៀងទាត់ ដើម្បីតាមដានកម្រិតសំណើម កម្រិតអាស៊ីត និងកំហាប់ឧស្ម័នរាវច្របាច់ដែលបង្ហាញពីការបំផ្លាញគ្រឿងបន្លាស់ខាងក្នុង។ ការត្រួតពិនិត្យថាមពលកំដៅ អាចរកឃើញចំណុចក្តៅ និងបញ្ហាការតភ្ជាប់មុនពេលវារីករាយទៅដល់ការខូចខាតគ្រឿងបរិក្ខារ ខណៈការត្រួតពិនិត្យការញ័រ អាចកំណត់បញ្ហាមេកានិចនៅក្នុងគ្រឿងបន្លាស់ចិត្តកណ្ដាល និងកូអ៊ីល។ បច្ចេកទេសរោគវិនិច្ឆ័យទាំងនេះ អនុញ្ញាតឱ្យធ្វើការសម្រេចចិត្តថែទាំដោយផ្អែកលើស្ថានភាព ដែលធ្វើឱ្យប្រសើរឡើងនូវស្ថេរភាព និងអាយុកាលបម្រើរបស់គ្រឿងបរិក្ខារ។
ការងារថែទាំប្រចាំថ្ងៃរួមមានការសម្អាតអ៊ីសូឡង់ និងប៊ើសុីង ការពិនិត្យការកំណត់សម្ពាធប្រឆាំង និងការផ្ទៀងផ្ទាត់ប្រតិបត្តិការប្រព័ន្ធកំដៅ និងឧបករណ៍ត្រួតពិនិត្យសីតុណ្ហភាព។ នីតិវិធីធ្វើតេស្តភ្លើងផ្ទៀងផ្ទាត់សុពលភាពអ៊ីសូឡង់ ភាពត្រឹមត្រូវនៃសមាមាត្រវិល និងលក្ខណៈភាពធន់ដែលប៉ះពាល់ដល់ប្រសិទ្ធភាព និងសុវត្ថិភាពរបស់ត្រង់ស្វូម័រ។ ការកត់ត្រាសកម្មភាពថែទាំ និងលទ្ធផលធ្វើតេស្តផ្តល់ទិន្នន័យប្រវត្តិសាស្ត្រដ៏មានតម្លៃសម្រាប់ការវិភាគនិន្នាការ និងការគ្រោងធ្វើការជំនួស។
នីតិវិធីឆ្លើយតបបន្ទាន់គួរដោះស្រាយបញ្ហាហូរប្រេង ស្ថានភាពសម្ពាធខ្ពស់ និងតម្រូវការបំពេញអគ្គិភ័យ ដើម្បីកាត់បន្ថយហានិភ័យសុវត្ថិភាព និងផលប៉ះពាល់បរិស្ថាន។ ការគ្រប់គ្រងស្តុកគ្រឿងបន្លាស់ធានាការមានគ្រឿងសំខាន់ៗដូចជាប៊ើសុីង សម្ពាធប្តូរតេប និងឧបករណ៍ត្រួតពិនិត្យ។ កម្មវិធីបណ្តុះបណ្តាលបុគ្គលិកថែទាំពង្រឹកការយល់ដឹងអំពីសុវត្ថិភាព និងសមត្ថភាពបច្ចេកទេសក្នុងនីតិវិធីថែទាំត្រង់ស្វូម័រ។
ការវិភាគសេដ្ឋកិច្ច និងផលតបសងវិនិយោគ
ការវិភាគថ្លៃដើមវដ្តជីវិតគិតគូរពីតម្លៃទិញដំបូង ការចំណាយក្នុងការដំឡើង ការចំណាយប្រតិបត្តិការ តម្រូវការថែទាំ និងការចំណាយចុងក្រោយសម្រាប់ការជំនួស ឬការបោះចោលក្នុងអំឡុងពេលអាយុកាលបម្រើរបស់ម៉ាស៊ីនបំលែង។ ពិន្ទុប្រសិទ្ធភាពថាមពលប៉ះពាល់យ៉ាងខ្លាំងដល់ថ្លៃប្រតិបត្តិការ ជាពិសេសសម្រាប់ម៉ាស៊ីនបំលែងដែលផ្ទុកបន្តដែលការកែលម្អប្រសិទ្ធភាពតិចតួចបង្កើតបាននូវការសន្សំយ៉ាងច្រើនតាមពេលវេលា។ ការព្យាករការកើនឡើងនៃការផ្ទុកប៉ះពាល់ដល់ការសម្រេចចិត្តទំហំ ហើយអាចធ្វើឱ្យការវិនិយោគដំបូងខ្ពស់ឡើងសម្រាប់ឯកតាដែលមានសមត្ថភាពធំជាងមានហេតុផល។
ថ្លៃដើមភាពអាចទុកចិត្តបានរួមមានការខាតបង់ផលិតកម្ម ការខូចខាតសម្ភារៈ និងឧប្បត្តិហេតុសុវត្ថិភាពដែលទាក់ទងនឹងការបរាជ័យរបស់ម៉ាស៊ីនបំលែង ឬការបិទសម្រាប់ការថែទាំយូរ។ កម្មវិធីដែលត្រូវការភាពអាចទុកចិត្តបានខ្ពស់អាចធ្វើឱ្យការរចនាម៉ាស៊ីនបំលែងថ្លៃថ្នូរមានហេតុផលដោយប្រព័ន្ធត្រួតពិនិត្យកែលម្អ និងលក្ខណៈពិសេសការពារបន្ថែម។ ការពិចារណាអំពីការធានារ៉ាប់រងអាចនឹងពេញចិត្តនឹងម៉ាស៊ីនបំលែងដែលមានកេត្តិ៍ស័ព្ទសុវត្ថិភាពល្អជាង និងគោរពតាមស្តង់ដារឧស្សាហកម្ម។
កត្តានៃការអស់សម័យនៃបច្ចេកវិទ្យារួមមានការមានវត្តមាននៃផ្នែកជំនួស សមត្ថភាពឆបគ្នាជាមួយប្រព័ន្ធការពារទំនើប និងតម្រូវការអនុលោមតាមបទបញ្ញាត្តិដែលអាចផ្លាស់ប្តូរតាមពេលវេលា។ ជម្រើសផ្នែកហិរញ្ញវត្ថុដូចជាការជួល ឬកិច្ចព្រមព្រៀងសេវាកម្មអាចផ្តល់ជម្រើសគួរឱ្យទាក់ទាញជាជាងការទិញដាច់សម្រាប់កម្មវិធីខ្លះ។ ការគណនាថ្លៃដើមសរុបនៃការកាន់កាប់គួររួមបញ្ចូលកត្តាទាក់ទងទាំងអស់ដើម្បីគាំទ្រការសម្រេចចិត្តទិញដោយមានចំណេះដឹង។
ស준្ឌិភាពនិងការត្រូវតាមតែការបញ្ជាក់
ស្តង់ដារឧស្សាហកម្ម និងតម្រូវការសញ្ញាប័ណ្ណ
ការផលិត និងការធ្វើតេស្តត្រង់ស្វើម័រ ត្រូវតែអនុវត្តតាមស្តង់ដារឧស្សាហកម្មដែលបានទទួលស្គាល់ ដូចជាស្តង់ដារ IEEE, IEC និង ANSI ដែលកំណត់នូវតម្រូវការប្រតិបត្តិការ លក្ខខណ្ឌសុវត្ថិភាព និងនីតិវិធីធានាគុណភាព។ ស្តង់ដារទាំងនេះកំណត់នូវតម្រូវការអប្បបរមាសម្រាប់ការរចនាអគ្គិសនី សំណង់មេកានិច និងសមត្ថភាពប្រតិបត្តិការក្នុងបរិស្ថាន ដែលធានាការប្រើប្រាស់បានសុវត្ថិភាព និងអាចទុកចិត្តបានក្រោមលក្ខខណ្ឌដែលបានកំណត់។ ការផ្តល់សញ្ញាប័ណ្ណដោយមន្ទីរពិសោធន៍ធ្វើតេស្តដែលបានទទួលស្គាល់ ផ្តល់នូវការបញ្ជាក់ឯករាជ្យអំពីការអនុវត្តតាមស្តង់ដារដែលពាក់ព័ន្ធ។
ស្តង់ដាសុវត្ថិភាពគ្របដណ្តប់លើការការពារអគ្គិភ័យ ការការពារការផ្ទះពូថ និងតម្រូវការសុវត្ថិភាពបុគ្គលិក រួមទាំងការដាក់ដីឱ្យបានត្រឹមត្រូវ ការសម្របសម្រួលសំភារៈការពារ និងនីតិវិធីបិទបញ្ចប់បន្ទាន់។ បទបញ្ញាត្តិបរិស្ថានគ្រប់គ្រងការដោះស្រាយ និងការចោលសារធាតុដែលមានសមត្ថភាពចុះខ្សោយ ជាពិសេសសម្ភារៈដែលមាន PCB ក្នុងម៉ាស៊ីនបំលែងចាស់ៗ។ តម្រូវការសុវត្ថិភាពនៅកន្លែងធ្វើការរួមមាននីតិវិធីបិទ-ដាក់ស្លាក (lockout/tagout) បទបញ្ញាត្តិសម្រាប់ចូលទៅកន្លែងគ្រប់គ្រងដោយរឹតត្បិត និងសេចក្តីកំណត់ស្តីពីសំភារៈការពារផ្ទាល់ខ្លួនសម្រាប់សកម្មភាពថែទាំ។
ប្រព័ន្ធគ្រប់គ្រងគុណភាពធានាថាមានដំណើរការផលិតកម្ម និងសមត្ថភាពផលិតផលដែលស្ថិតក្នុងស្ថានភាពស៊ីសង្វាក់គ្នាតាមរយៈនីតិវិធីដែលបានកត់ត្រា ការគ្រប់គ្រងសម្ភារៈ និងការចាត់វិធានការបន្តបន្ទាប់ដើម្បីកែលម្អ។ ការត្រួតពិនិត្យដោយភាគីទីបី និងការធ្វើតេស្តក្រោមការសង្កេត ផ្តល់ការធានាបន្ថែមអំពីគុណភាពផលិតផល និងការគោរពតាមសេចក្តីកំណត់គម្រោង។ លក្ខខណ្ឌធានា និងសមត្ថភាពគាំទ្រសេវាកម្ម ឆ្លុះបញ្ចាំងពីភាពជឿជាក់របស់អ្នកផលិតចំពោះភាពអាចទុកចិត្តបាន និងការពេញចិត្តរបស់អតិថិជន។
នីតិវិធីដំឡើង និងដាក់ឱ្យដំណើរការ
ការដំឡើងដោយអ្នកជំនាញទាមទារឱ្យមានអ្នកទំនាក់ទំនងផ្នែកអគ្គិសនីដែលមានសុពលភាព និងបទពិសោធន៍ក្នុងការដំណើរការត្រាស្វូរ៉ម៉ែរ និងនីតិវិធីតភ្ជាប់ និងប្រូតូកោលសាកល្បង ដើម្បីធានាបាននូវប្រតិបត្តិការដែលមានសុវត្ថិភាព និងអាចទុកចិត្តបាន។ ការរៀបចំទីតាំងរួមមានការរចនាមូលដ្ឋាន ការដាក់ខ្សែកាប ការដំឡើងសម្ភារៈការពារ និងការសម្របសម្រួលតាមតម្រូវការតភ្ជាប់បណ្តាញប្រើប្រាស់។ សម្ភារៈដែលប្រើសម្រាប់ការដោះដូរ និងដាក់ទីតាំងឱ្យបានត្រឹមត្រូវនឹងការពារការខូចខាតកំឡុងពេលដំឡើង ហើយធានាសុវត្ថិភាពបុគ្គលិកផងដែរ។
នីតិវិធីដំឡើងបញ្ចប់ផ្ទៀងផ្ទាត់ពីការដំឡើងត្រឹមត្រូវ ការតភ្ជាប់អគ្គិសនី និងការសម្របសម្រួលឧបករណ៍ការពារមុនពេលផ្តល់ថាមពលដល់ត្រាស្វូរ៉ម៉ែរ និងបន្ទុកដែលតភ្ជាប់។ ការសាកល្បងទទួលយកបញ្ជាក់ពីការគោរពតាមសេចក្តីបញ្ជាក់ និងកំណត់ភាពខុសប្រក្រតីណាមួយក្នុងការដំឡើងដែលត្រូវកែតម្រូវ។ ការឯកសារនៃសកម្មភាពដំឡើង និងសាកល្បងផ្តល់ទិន្នន័យដើមសម្រាប់សកម្មភាពថែទាំ និងការដោះស្រាយបញ្ហានាពេលអនាគត។
ការបណ្តុះបណ្តាលប្រតិបត្តិករធានាថាបុគ្គលិកក្នុងស្ថាប័នយល់ដឹងអំពីនីតិវិធីប្រតិបត្តិធម្មតា ប្រតិបត្តិការប្រតិកម្មបន្ទាន់ និងតម្រូវការថែទាំប្រចាំថ្ងៃ។ ការគាំទ្របន្តពីអ្នកផលិត ឬអ្នកផ្តល់សេវាកម្ម អាចរួមមានសមត្ថភាពតាមដានពីចម្ងាយ ជំនួយបច្ចេកទេស និងសេវាកម្មជួសជុលបន្ទាន់។ ការឯកសារកម្ម និងការកត់ត្រាដែលត្រឹមត្រូវ គាំទ្រដល់ការទាមទារធានារ៉ាប់រង និងតម្រូវការអនុលោមតាមបទបញ្ញត្តិ។
សំណួរញឹកញាប់
តើកត្តាអ្វីខ្លះកំណត់ទំហំដែលសមស្របសម្រាប់ការដំឡើងត្រានស្វើមប្រេង?
ការកំណត់ទំហំត្រង់ស្វើម៉ែតដែលត្រឹមត្រូវ ទាមទារឱ្យគណនាទំហំបន្ទុកសរុបដែលបានភ្ជាប់ ដាក់ប្រើប្រាស់កត្តាតម្រូវការ និងភាពចម្រុះដែលសមស្រប និងពិចារណាលើតម្រូវការពង្រីកនាពេលអនាគត។ ត្រង់ស្វើម៉ែតត្រូវតែអាចទប់ទល់នឹងលក្ខខណ្ឌប្រតិបត្តិការធម្មតា ខណៈពេលដែលផ្តល់សមត្ថភាពគ្រប់គ្រាន់សម្រាប់ការប្រើប្រាស់កំពូល និងចរន្តចាប់ផ្តើមរបស់ម៉ូទ័រ។ ការសិក្សាបន្ទុកដោយអ្នកជំនាញ វិភាគលើគំរូនៃការប្រើប្រាស់កន្លងមក សេចក្តីបញ្ជាក់បច្ចេកទេសរបស់បរិក្ខារ និងការព្យាករណ៍ការរីកចម្រើន ដើម្បីកំណត់លក្ខខណ្ឌកំណត់ទំហំដែលល្អបំផុត ដែលធានាភាពសមស្របរវាងតម្រូវការប្រតិបត្តិការ និងកត្តាសេដ្ឋកិច្ច។
តើលក្ខខណ្ឌបរិស្ថានប៉ះពាល់ដល់ប្រសិទ្ធភាព និងការជ្រើសរើសត្រង់ស្វើម៉ែតប្រេងដោយរបៀបណា
កត្តាបរិស្ថានដូចជាសីតុណ្ហភាពបរិយាកាស សំណើម កំពស់លើសមុទ្រ និងកម្រិតការបំពុល មានឥទ្ធិពលយ៉ាងខ្លាំងដល់តម្រូវការការរចនាម៉ាស៊ីនបំប្លែង និងលក្ខណៈប្រតិបត្តិការ។ សីតុណ្ហភាពខ្ពស់ធ្វើឱ្យសមត្ថភាពផ្ទុកថយចុះ ហើយបំភាន់ការចាស់របស់ស្រទាប់ច្រកភ្លើង ខណៈពេលដែលអាកាសធាតុត្រជាក់ខ្លាំងប៉ះពាល់ដល់ភាពជាប់របស់ប្រេង និងលក្ខណៈចាប់ផ្តើម។ បរិយាកាសដែលបំផ្លាញតម្រូវឱ្យមានសំណាញ់ការពារបន្ថែម និងការរចនាដែលបិទជិតបានល្អ ខណៈដែលសកម្មភាពរញ្ជួយដីតម្រូវឱ្យមានប្រព័ន្ធដំឡើងពិសេស និងការពង្រឹងរចនាសម្ព័ន្ធ។
អ្វីគឺជាការអនុវត្តការថែទាំដែលអាចពន្យារអាយុកាលប្រើប្រាស់ និងស្ថេរភាពរបស់ម៉ាស៊ីនបំប្លែងប្រេង
កម្មវិធីថែទាំដែលមានប្រសិទ្ធភាព រួមមានការធ្វើតេស្តប្រេងជាប្រចាំសម្រាប់កំហាប់សើម កំហាប់អាស៊ីត និងឧស្ម័នរាវដែលបញ្ជាក់ពីការខូចខាតខាងក្នុង។ ការត្រួតពិនិត្យដោយថេរម៉ូក្រាហ្វិក (Thermographic inspections) អាចរកឃើញបញ្ហាការតភ្ជាប់ និងកន្លែងក្តៅមុនពេលបរាជ័យកើតឡើង ខណៈការធ្វើតេស្តអគ្គិសនីផ្ទៀងផ្ទាត់ភាពសុចរិតរបស់ស្រទាប់ការពារ និងលក្ខណៈប្រតិបត្តិការ។ ការឯកសារដោយត្រឹមត្រូវ ការគ្រប់គ្រងគ្រឿងបន្លាស់ និងការបណ្តុះបណ្តាលបុគ្គលិក ធានាគុណភាពការថែទាំដែលស៊ីសង្វាក់គ្នា និងគាំទ្រយុទ្ធសាស្ត្រថែទាំបែបទស្សន៍ទាយ ដែលធ្វើឱ្យភាពអាចទុកចិត្តបានរបស់បរិក្ខារមានប្រសិទ្ធភាពបំផុត។
តើកត្តាសុវត្ថិភាពអ្វីខ្លះដែលចាំបាច់សម្រាប់ការដំឡើងត្រង់ហ្វូម៉ែរប្រេង?
តម្រូវការសុវត្ថិភាពរួមមានការការពារអគ្គិភ័យតាមរយៈការដាក់ចន្លោះឱ្យបានត្រឹមត្រូវ និងប្រព័ន្ធបញ្ចេញអគ្គិភ័យ ការការពារបរិស្ថានពីការហូរចេញនៃប្រេងដែលអាចកើតមាន និងការការពារបុគ្គលិកតាមរយៈរបាំង និងប្រព័ន្ធសញ្ញាគ្រោះថ្នាក់ដែលសមស្រប។ ការដាក់បន្ទាត់ដីឱ្យបានត្រឹមត្រូវ ការសម្របសម្រួលឧបករណ៍ការពារ និងនីតិវិធីបន្ទាន់ ជួយកាត់បន្ថយហានិភ័យដែលទាក់ទងនឹងកំហុសផ្នែកអគ្គិសនី និងការខូចខាតរបស់សម្ភារៈ។ ការគោរពតាមក្បួន និងស្តង់ដារពាក់ព័ន្ធធានាថាការដំឡើងបំពេញតាមតម្រូវការអប្បបរមាស្តីពីសុវត្ថិភាព ខណៈដែលកត្តាស្តីពីធានារ៉ាប់រង និងការទទួលខុសត្រូវអាចជាមូលហេតុគាំទ្រសម្រាប់វិធានការការពារដែលបានពង្រឹង។
ទំព័រ ដើម
- ការយល់ដឹងអំពីបច្ចេកវិទ្យា និងកម្មវិធីម៉ាស៊ីនបំលែងភ្លើង
- សេចក្តីបញ្ជាក់បច្ចេកទេស និងលក្ខខណ្ឌប្រតិបត្តិការ
- ការថែទាំ និងការវិភាគថ្លៃដើមអាយុកាល
- ស준្ឌិភាពនិងការត្រូវតាមតែការបញ្ជាក់
-
សំណួរញឹកញាប់
- តើកត្តាអ្វីខ្លះកំណត់ទំហំដែលសមស្របសម្រាប់ការដំឡើងត្រានស្វើមប្រេង?
- តើលក្ខខណ្ឌបរិស្ថានប៉ះពាល់ដល់ប្រសិទ្ធភាព និងការជ្រើសរើសត្រង់ស្វើម៉ែតប្រេងដោយរបៀបណា
- អ្វីគឺជាការអនុវត្តការថែទាំដែលអាចពន្យារអាយុកាលប្រើប្រាស់ និងស្ថេរភាពរបស់ម៉ាស៊ីនបំប្លែងប្រេង
- តើកត្តាសុវត្ថិភាពអ្វីខ្លះដែលចាំបាច់សម្រាប់ការដំឡើងត្រង់ហ្វូម៉ែរប្រេង?